Note
Click here to download the full example code
03. Monodepth2 training on KITTI dataset¶
This is a tutorial of training MonoDepth2 on the KITTI dataset using Gluon CV toolkit. The readers should have basic knowledge of deep learning and should be familiar with Gluon API. New users may first go through A 60-minute Gluon Crash Course. You can Start Training Now or Dive into Deep.
Start Training Now¶
Hint
Feel free to skip the tutorial because the training script is self-complete and ready to launch.
Download Full Python Script: train.py
Download Full Python Script: trainer.py
mono+stereo mode training command:
python train.py --model_zoo monodepth2_resnet18_kitti_mono_stereo_640x192 --model_zoo_pose monodepth2_resnet18_posenet_kitti_mono_stereo_640x192 --pretrained_base --frame_ids 0 -1 1 --use_stereo --log_dir ./tmp/mono_stereo/ --png --gpu 0 --batch_size 8
mono mode training command:
python train.py --model_zoo monodepth2_resnet18_kitti_mono_640x192 --model_zoo_pose monodepth2_resnet18_posenet_kitti_mono_640x192 --pretrained_base --log_dir ./tmp/mono/ --png --gpu 0 --batch_size 12
stereo mode training command:
python train.py --model_zoo monodepth2_resnet18_kitti_stereo_640x192 --pretrained_base --split eigen_full --frame_ids 0 --use_stereo --log_dir ./tmp/stereo/ --png --gpu 0 --batch_size 12
For more training command options, please run python train.py -h
Please checkout the model_zoo for training commands of reproducing the pretrained model.
Dive into Deep¶
import numpy as np
import mxnet as mx
from mxnet import gluon, autograd
import gluoncv
Digging into Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Prediction¶
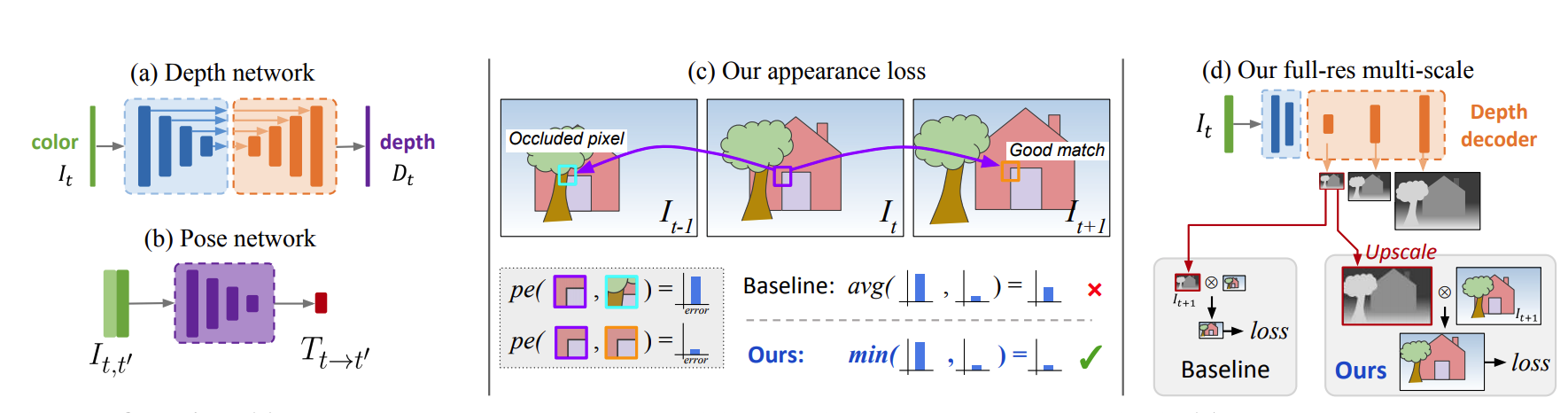
(figure credit to Godard et al. )
Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation (Monodepth2) [Godard19] builds a simple depth model and train it with a self-supervised manner by exploiting the spatial geometry constrain. The key idea of Monodepth2 is that it builds a novel reprojection loss, include (1) a minimum reprojection loss, designed to robustly handle occlusions, (2) a full-resolution multi-scale sampling method that reduces visual artifacts, and (3) an auto-masking loss to ignore training pixels that violate camera motion assumptions.
Monodepth2 Model¶
A simple U-Net architecture is used in Monodepth2, which combines multiple scale features with different receptive field sizes. It pools the feature maps into different sizes and then concatenating together after upsampling. There are two decoders for depth estimation and camera pose estimation.
The encoder module is a ResNet, it accepts single RGB images as input for the depth model. For the pose model, The pose encoder is modified to accept a pair of frames, or six channels, as input. Therefore, the pose encoder has convolutional weights in the first layer of shape 6×64×3×3, instead of the ResNet default of 3×64×3×3. When using pre-trained weights for the pose encoder, the first pre-trained filter tensor is duplicated along the channel dimension to make a filter of shape 6 × 64 × 3 × 3. All weights in this new expanded filter are divided by 2 to make the output of the convolution in the same numerical range as the original, one-image ResNet.
The encoder is defined as:
class ResnetEncoder(nn.HybridBlock):
def __init__(self, backbone, pretrained, num_input_images=1,
root=os.path.join(os.path.expanduser('~'), '.mxnet/models'),
ctx=cpu(), **kwargs):
super(ResnetEncoder, self).__init__()
self.num_ch_enc = np.array([64, 64, 128, 256, 512])
resnets = {'resnet18': resnet18_v1b,
'resnet34': resnet34_v1b,
'resnet50': resnet50_v1s,
'resnet101': resnet101_v1s,
'resnet152': resnet152_v1s}
num_layers = {'resnet18': 18,
'resnet34': 34,
'resnet50': 50,
'resnet101': 101,
'resnet152': 152}
if backbone not in resnets:
raise ValueError("{} is not a valid resnet".format(backbone))
if num_input_images > 1:
self.encoder = resnets[backbone](pretrained=False, ctx=ctx, **kwargs)
if pretrained:
filename = os.path.join(
root, 'resnet%d_v%db_multiple_inputs.params' % (num_layers[backbone], 1))
if not os.path.isfile(filename):
from ..model_store import get_model_file
loaded = mx.nd.load(get_model_file('resnet%d_v%db' % (num_layers[backbone], 1),
tag=pretrained, root=root))
loaded['conv1.weight'] = mx.nd.concat(
*([loaded['conv1.weight']] * num_input_images), dim=1) / num_input_images
mx.nd.save(filename, loaded)
self.encoder.load_parameters(filename, ctx=ctx)
from ...data import ImageNet1kAttr
attrib = ImageNet1kAttr()
self.encoder.synset = attrib.synset
self.encoder.classes = attrib.classes
self.encoder.classes_long = attrib.classes_long
else:
self.encoder = resnets[backbone](pretrained=pretrained, ctx=ctx, **kwargs)
if backbone not in ('resnet18', 'resnet34'):
self.num_ch_enc[1:] *= 4
def hybrid_forward(self, F, input_image):
self.features = []
x = (input_image - 0.45) / 0.225
x = self.encoder.conv1(x)
x = self.encoder.bn1(x)
self.features.append(self.encoder.relu(x))
self.features.append(self.encoder.layer1(self.encoder.maxpool(self.features[-1])))
self.features.append(self.encoder.layer2(self.features[-1]))
self.features.append(self.encoder.layer3(self.features[-1]))
self.features.append(self.encoder.layer4(self.features[-1]))
return self.features
The Decoder module is a fully convolutional network with skip architecture, it exploits the feature maps in a different scale and concatenating together after upsampling. A sigmoid activation at the last layer. It bound the output to [0, 1], which means that the depth decoder outputs a normalized disparity map.
It is defined as:
class DepthDecoder(nn.HybridBlock):
def __init__(self, num_ch_enc, scales=range(4), num_output_channels=1,
use_skips=True):
super(DepthDecoder, self).__init__()
self.num_output_channels = num_output_channels
self.use_skips = use_skips
self.upsample_mode = 'nearest'
self.scales = scales
self.num_ch_enc = num_ch_enc
self.num_ch_dec = np.array([16, 32, 64, 128, 256])
# decoder
with self.name_scope():
self.convs = OrderedDict()
for i in range(4, -1, -1):
# upconv_0
num_ch_in = self.num_ch_enc[-1] if i == 4 else self.num_ch_dec[i + 1]
num_ch_out = self.num_ch_dec[i]
self.convs[("upconv", i, 0)] = ConvBlock(num_ch_in, num_ch_out)
# upconv_1
num_ch_in = self.num_ch_dec[i]
if self.use_skips and i > 0:
num_ch_in += self.num_ch_enc[i - 1]
num_ch_out = self.num_ch_dec[i]
self.convs[("upconv", i, 1)] = ConvBlock(num_ch_in, num_ch_out)
for s in self.scales:
self.convs[("dispconv", s)] = Conv3x3(
self.num_ch_dec[s], self.num_output_channels)
# register blocks
for k in self.convs:
self.register_child(self.convs[k])
self.decoder = nn.HybridSequential()
self.decoder.add(*list(self.convs.values()))
self.sigmoid = nn.Activation('sigmoid')
def hybrid_forward(self, F, input_features):
self.outputs = []
# decoder
x = input_features[-1]
for i in range(4, -1, -1):
x = self.convs[("upconv", i, 0)](x)
x = [F.UpSampling(x, scale=2, sample_type='nearest')]
if self.use_skips and i > 0:
x += [input_features[i - 1]]
x = F.concat(*x, dim=1)
x = self.convs[("upconv", i, 1)](x)
if i in self.scales:
self.outputs.append(self.sigmoid(self.convs[("dispconv", i)](x)))
return self.outputs
The PoseNet Decoder module is a fully convolutional network and it predicts the rotation using an axis-angle representation and scale the rotation and translation outputs by 0.01.
It is defined as:
class PoseDecoder(nn.HybridBlock):
def __init__(self, num_ch_enc, num_input_features, num_frames_to_predict_for=2, stride=1):
super(PoseDecoder, self).__init__()
self.num_ch_enc = num_ch_enc
self.num_input_features = num_input_features
if num_frames_to_predict_for is None:
num_frames_to_predict_for = num_input_features - 1
self.num_frames_to_predict_for = num_frames_to_predict_for
self.convs = OrderedDict()
self.convs[("squeeze")] = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=self.num_ch_enc[-1], channels=256, kernel_size=1)
self.convs[("pose", 0)] = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=num_input_features * 256, channels=256,
kernel_size=3, strides=stride, padding=1)
self.convs[("pose", 1)] = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=256, channels=256, kernel_size=3, strides=stride, padding=1)
self.convs[("pose", 2)] = nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=256, channels=6 * num_frames_to_predict_for, kernel_size=1)
# register blocks
for k in self.convs:
self.register_child(self.convs[k])
self.net = nn.HybridSequential()
self.net.add(*list(self.convs.values()))
def hybrid_forward(self, F, input_features):
last_features = [f[-1] for f in input_features]
cat_features = [F.relu(self.convs["squeeze"](f)) for f in last_features]
cat_features = F.concat(*cat_features, dim=1)
out = cat_features
for i in range(3):
out = self.convs[("pose", i)](out)
if i != 2:
out = F.relu(out)
out = out.mean(3).mean(2)
out = 0.01 * out.reshape(-1, self.num_frames_to_predict_for, 1, 6)
axisangle = out[..., :3]
translation = out[..., 3:]
return axisangle, translation
Monodepth model is provided in gluoncv.model_zoo.MonoDepth2 and PoseNet is provide
in gluoncv.model_zoo.MonoDepth2PoseNet. To get Monodepth2 model using ResNet18 base network:
model = gluoncv.model_zoo.get_monodepth2(backbone='resnet18')
print(model)
Out:
MonoDepth2(
(encoder): ResnetEncoder(
(encoder): ResNetV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(3 -> 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), padding=(3, 3), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu): Activation(relu)
(maxpool): MaxPool2D(size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), ceil_mode=False, global_pool=False, pool_type=max, layout=NCHW)
(layer1): HybridSequential(
(0): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(64 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(64 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
(1): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(64 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(64 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
)
(layer2): HybridSequential(
(0): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(64 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(128 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(64 -> 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
)
)
(1): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(128 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(128 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
)
(layer3): HybridSequential(
(0): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(128 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(256 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(128 -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
)
)
(1): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(256 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(256 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
)
(layer4): HybridSequential(
(0): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(256 -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(512 -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(256 -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
)
)
(1): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(512 -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(512 -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
)
(avgpool): GlobalAvgPool2D(size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), ceil_mode=True, global_pool=True, pool_type=avg, layout=NCHW)
(flat): Flatten
(fc): Dense(512 -> 1000, linear)
)
)
(decoder): DepthDecoder(
(decoder): HybridSequential(
(0): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(512 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(1): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(512 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(2): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(256 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(3): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(256 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(4): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(128 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(5): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(128 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(6): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(64 -> 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(7): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(96 -> 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(8): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(32 -> 16, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(9): ConvBlock(
(conv): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(16 -> 16, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(nonlin): ELU(
)
)
(10): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(16 -> 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(11): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(32 -> 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(12): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(64 -> 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
(13): Conv3x3(
(pad): ReflectionPad2D(
)
(conv): Conv2D(128 -> 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
)
)
(sigmoid): Activation(sigmoid)
)
)
To get PoseNet using ResNet18 base network:
posenet = gluoncv.model_zoo.get_monodepth2posenet(backbone='resnet18')
print(posenet)
Out:
MonoDepth2PoseNet(
(encoder): ResnetEncoder(
(encoder): ResNetV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(6 -> 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), padding=(3, 3), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu): Activation(relu)
(maxpool): MaxPool2D(size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), ceil_mode=False, global_pool=False, pool_type=max, layout=NCHW)
(layer1): HybridSequential(
(0): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(64 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(64 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
(1): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(64 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(64 -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=64)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
)
(layer2): HybridSequential(
(0): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(64 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(128 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(64 -> 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
)
)
(1): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(128 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(128 -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=128)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
)
(layer3): HybridSequential(
(0): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(128 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(256 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(128 -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
)
)
(1): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(256 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(256 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
)
(layer4): HybridSequential(
(0): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(256 -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(512 -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(256 -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
)
)
(1): BasicBlockV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(512 -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(512 -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=False, in_channels=512)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
)
)
(avgpool): GlobalAvgPool2D(size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0), ceil_mode=True, global_pool=True, pool_type=avg, layout=NCHW)
(flat): Flatten
(fc): Dense(512 -> 1000, linear)
)
)
(decoder): PoseDecoder(
(net): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(512 -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(1): Conv2D(256 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(2): Conv2D(256 -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): Conv2D(256 -> 12, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
)
)
Dataset and Data Augmentation¶
Prepare KITTI RAW Dataset:
Here we give an example of training monodepth2 on the KITTI RAW dataset [Godard19]. First, we need to prepare the dataset. The official implementation of monodepth2 does not use all the data of the KITTI RAW dataset, here we use the same dataset and split method as [Godard19]. You need download the split zip file, and extract it to
$(HOME)/.mxnet/datasets/kitti/.Follow the command to get the dataset:
cd ~ mkdir -p .mxnet/datasets/kitti cd .mxnet/datasets/kitti wget https://github.com/KuangHaofei/GluonCV_Test/raw/master/monodepthv2/tutorials/splits.zip unzip splits.zip wget -i splits/kitti_archives_to_download.txt -P kitti_data/ cd kitti_data unzip "*.zip"
Hint
You need 175GB, free disk space to download and extract this dataset. SSD harddrives are recommended for faster speed. The time it takes to prepare the dataset depends on your Internet connection and disk speed. For example, it takes around 2 hours on an AWS EC2 instance with EBS.
We provide self-supervised depth estimation datasets in gluoncv.data.
For example, we can easily get the KITTI RAW Stereo dataset:
import os
from gluoncv.data.kitti import readlines, dict_batchify_fn
train_filenames = os.path.join(
os.path.expanduser("~"), '.mxnet/datasets/kitti/splits/eigen_full/train_files.txt')
train_filenames = readlines(train_filenames)
train_dataset = gluoncv.data.KITTIRAWDataset(
filenames=train_filenames, height=192, width=640,
frame_idxs=[0, -1, 1, "s"], num_scales=4, is_train=True, img_ext='.png')
print('Training images:', len(train_dataset))
# set batch_size = 12 for toy example
batch_size = 12
train_loader = gluon.data.DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, batchify_fn=dict_batchify_fn,
num_workers=12, pin_memory=True, last_batch='discard')
Here, the frame_idxs argument is used to decide the input frame. It is a list and the first element
must be 0 means source frame. Other elements mean target frames. Numerical values represent relative frame id in
image sequences. “s” means another side of the source image upon stereo pairs.
Data Augmentation
We follow the standard data augmentation routine to transform the input image. Here, we just use RandomFlip with 50% probability for input images.
Random pick one example for visualization:
import random
from datetime import datetime
random.seed(datetime.now())
idx = random.randint(0, len(train_dataset))
data = train_dataset[idx]
input_img = data[("color", 0, 0)]
input_stereo_img = data[("color", 's', 0)]
input_gt = data['depth_gt']
input_img = np.transpose((input_img.asnumpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8), (1, 2, 0))
input_stereo_img = np.transpose((input_stereo_img.asnumpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8), (1, 2, 0))
input_gt = np.transpose((input_gt.asnumpy()).astype(np.uint8), (1, 2, 0))
from PIL import Image
input_img = Image.fromarray(input_img)
input_stereo_img = Image.fromarray(input_stereo_img)
input_gt = Image.fromarray(input_gt[:, :, 0])
input_img.save("input_img.png")
input_stereo_img.save("input_stereo_img.png")
input_gt.save("input_gt.png")
Plot the stereo image pairs and ground truth of the left image:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
input_img = Image.open('input_img.png').convert('RGB')
input_stereo_img = Image.open('input_stereo_img.png').convert('RGB')
input_gt = Image.open('input_gt.png')
fig = plt.figure()
# subplot 1 for left image
plt.subplots_adjust(left=None, bottom=None, right=None, top=None, wspace=None, hspace=0.75)
fig.add_subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.title("left image")
plt.imshow(input_img)
# subplot 2 for right images
fig.add_subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.title("right image")
plt.imshow(input_stereo_img)
# subplot 3 for the ground truth
fig.add_subplot(3, 1, 3)
plt.title("ground truth of left input (the reprojection of LiDAR data)")
plt.imshow(input_gt)
# display
plt.show()
The Dataloader will provide a dictionary which includes raw images, augmented images, camera intrinsics, camera extrinsic (stereo), and ground truth depth maps (for validation).
Training Details¶
Predict Camera Pose:
When training network with mono or mono+stereo mode, we have to get the predicted camera pose through PoseNet.
The prediction of loss is defined as
(Please check out the full trainer.py for complete implementation.):
def predict_poses(self, inputs):
outputs = {}
pose_feats = {f_i: inputs["color_aug", f_i, 0] for f_i in self.opt.frame_ids}
for f_i in self.opt.frame_ids[1:]:
if f_i != "s":
# To maintain ordering we always pass frames in temporal order
if f_i < 0:
pose_inputs = [pose_feats[f_i], pose_feats[0]]
else:
pose_inputs = [pose_feats[0], pose_feats[f_i]]
axisangle, translation = self.posenet(mx.nd.concat(*pose_inputs, dim=1))
outputs[("axisangle", 0, f_i)] = axisangle
outputs[("translation", 0, f_i)] = translation
# Invert the matrix if the frame id is negative
outputs[("cam_T_cam", 0, f_i)] = transformation_from_parameters(
axisangle[:, 0], translation[:, 0], invert=(f_i < 0))
return outputs
Image Reconstruction:
For training the network via self-supervised manner, we have to reconstruct a source image from target image according to predicted depth and pose (or use camera extrinsic of stereo pairs). Then, calculating reprojection photometric loss between the reconstructed source image with the real source image.
The whole process is divided into three steps,
To back project each point of the target image to 3D space according to depth and camera intrinsic;
To project 3D points to image plane according to camera extrinsic (pose) and intrinsic;
Sampling pixels from the source image to reconstruct a new image according to the projected points (exploit Spatial Transformer Networks (STN) to ensure that the sampling is differentiable).
Back projection (2D to 3D) is defined as:
class BackprojectDepth(nn.HybridBlock):
"""Layer to transform a depth image into a point cloud
"""
def __init__(self, batch_size, height, width, ctx=mx.cpu()):
super(BackprojectDepth, self).__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.height = height
self.width = width
self.ctx = ctx
meshgrid = np.meshgrid(range(self.width), range(self.height), indexing='xy')
id_coords = np.stack(meshgrid, axis=0).astype(np.float32)
id_coords = mx.nd.array(id_coords).as_in_context(self.ctx)
pix_coords = mx.nd.expand_dims(mx.nd.stack(*[id_coords[0].reshape(-1),
id_coords[1].reshape(-1)], axis=0),
axis=0)
pix_coords = pix_coords.repeat(repeats=batch_size, axis=0)
pix_coords = pix_coords.as_in_context(self.ctx)
with self.name_scope():
self.id_coords = self.params.get('id_coords', shape=id_coords.shape,
init=mx.init.Zero(), grad_req='null')
self.id_coords.initialize(ctx=self.ctx)
self.id_coords.set_data(mx.nd.array(id_coords))
self.ones = self.params.get('ones',
shape=(self.batch_size, 1, self.height * self.width),
init=mx.init.One(), grad_req='null')
self.ones.initialize(ctx=self.ctx)
self.pix_coords = self.params.get('pix_coords',
shape=(self.batch_size, 3, self.height * self.width),
init=mx.init.Zero(), grad_req='null')
self.pix_coords.initialize(ctx=self.ctx)
self.pix_coords.set_data(mx.nd.concat(pix_coords, self.ones.data(), dim=1))
def hybrid_forward(self, F, depth, inv_K, **kwargs):
cam_points = F.batch_dot(inv_K[:, :3, :3], self.pix_coords.data())
cam_points = depth.reshape(self.batch_size, 1, -1) * cam_points
cam_points = F.concat(cam_points, self.ones.data(), dim=1)
return cam_points
Projection (3D to 2D) is defined as:
class Project3D(nn.HybridBlock):
"""Layer which projects 3D points into a camera with intrinsics K and at position T
"""
def __init__(self, batch_size, height, width, eps=1e-7):
super(Project3D, self).__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.height = height
self.width = width
self.eps = eps
def hybrid_forward(self, F, points, K, T):
P = F.batch_dot(K, T)[:, :3, :]
cam_points = F.batch_dot(P, points)
cam_pix = cam_points[:, :2, :] / (cam_points[:, 2, :].expand_dims(1) + self.eps)
cam_pix = cam_pix.reshape(self.batch_size, 2, self.height, self.width)
x_src = cam_pix[:, 0, :, :] / (self.width - 1)
y_src = cam_pix[:, 1, :, :] / (self.height - 1)
pix_coords = F.concat(x_src.expand_dims(1), y_src.expand_dims(1), dim=1)
pix_coords = (pix_coords - 0.5) * 2
return pix_coords
The image reconstruction function is defined as
(Please check out the full trainer.py for complete implementation.):
def generate_images_pred(self, inputs, outputs):
for scale in self.opt.scales:
disp = outputs[("disp", scale)]
if self.opt.v1_multiscale:
source_scale = scale
else:
disp = mx.nd.contrib.BilinearResize2D(disp,
height=self.opt.height,
width=self.opt.width)
source_scale = 0
_, depth = disp_to_depth(disp, self.opt.min_depth, self.opt.max_depth)
outputs[("depth", 0, scale)] = depth
for i, frame_id in enumerate(self.opt.frame_ids[1:]):
if frame_id == "s":
T = inputs["stereo_T"]
else:
T = outputs[("cam_T_cam", 0, frame_id)]
cam_points = self.backproject_depth[source_scale](depth,
inputs[("inv_K", source_scale)])
pix_coords = self.project_3d[source_scale](cam_points,
inputs[("K", source_scale)],
T)
outputs[("sample", frame_id, scale)] = pix_coords
outputs[("color", frame_id, scale)] = mx.nd.BilinearSampler(
data=inputs[("color", frame_id, source_scale)],
grid=outputs[("sample", frame_id, scale)],
name='sampler')
if not self.opt.disable_automasking:
outputs[("color_identity", frame_id, scale)] = \
inputs[("color", frame_id, source_scale)]
Training Losses:
We apply a standard reprojection loss to train Monodepth2. As describes in Monodepth2 [Godard19] , the reprojection loss includes three parts: a multi-scale reprojection photometric loss (combined L1 loss and SSIM loss), an auto-masking loss and an edge-aware smoothness loss as in Monodepth [Godard17] .
The computation of loss is defined as
(Please checkout the full trainer.py for complete implementation.):
def compute_losses(self, inputs, outputs):
"""Compute the reprojection and smoothness losses for a minibatch
"""
losses = {}
total_loss = 0
for scale in self.opt.scales:
loss = 0
reprojection_losses = []
if self.opt.v1_multiscale:
source_scale = scale
else:
source_scale = 0
disp = outputs[("disp", scale)]
color = inputs[("color", 0, scale)]
target = inputs[("color", 0, source_scale)]
for frame_id in self.opt.frame_ids[1:]:
pred = outputs[("color", frame_id, scale)]
reprojection_losses.append(self.compute_reprojection_loss(pred, target))
reprojection_losses = mx.nd.concat(*reprojection_losses, dim=1)
if not self.opt.disable_automasking:
identity_reprojection_losses = []
for frame_id in self.opt.frame_ids[1:]:
pred = inputs[("color", frame_id, source_scale)]
identity_reprojection_losses.append(
self.compute_reprojection_loss(pred, target))
identity_reprojection_losses = mx.nd.concat(*identity_reprojection_losses, dim=1)
if self.opt.avg_reprojection:
identity_reprojection_loss = \
identity_reprojection_losses.mean(axis=1, keepdims=True)
else:
# save both images, and do min all at once below
identity_reprojection_loss = identity_reprojection_losses
if self.opt.avg_reprojection:
reprojection_loss = reprojection_losses.mean(axis=1, keepdims=True)
else:
reprojection_loss = reprojection_losses
if not self.opt.disable_automasking:
# add random numbers to break ties
identity_reprojection_loss = \
identity_reprojection_loss + \
mx.nd.random.randn(*identity_reprojection_loss.shape).as_in_context(
identity_reprojection_loss.context) * 0.00001
combined = mx.nd.concat(identity_reprojection_loss, reprojection_loss, dim=1)
else:
combined = reprojection_loss
if combined.shape[1] == 1:
to_optimise = combined
else:
to_optimise = mx.nd.min(data=combined, axis=1)
idxs = mx.nd.argmin(data=combined, axis=1)
if not self.opt.disable_automasking:
outputs["identity_selection/{}".format(scale)] = (
idxs > identity_reprojection_loss.shape[1] - 1).astype('float')
loss += to_optimise.mean()
mean_disp = disp.mean(axis=2, keepdims=True).mean(axis=3, keepdims=True)
norm_disp = disp / (mean_disp + 1e-7)
smooth_loss = get_smooth_loss(norm_disp, color)
loss = loss + self.opt.disparity_smoothness * smooth_loss / (2 ** scale)
total_loss = total_loss + loss
losses["loss/{}".format(scale)] = loss
total_loss = total_loss / self.num_scales
losses["loss"] = total_loss
return losses
Learning Rate and Scheduling:
Here, we follow the standard strategy of monodepth2. The network is trained for 20 epochs using Adam. We use a ‘step’ learning rate scheduler for Monodepth2 training, provided in
gluoncv.utils.LRScheduler. We use a learning rate of 10−4 for the first 15 epochs which is then dropped to 10−5 for the remainder.
The example of optimization is defined as:
lr_scheduler = gluoncv.utils.LRSequential([
gluoncv.utils.LRScheduler(
'step', base_lr=1e-4, nepochs=20, iters_per_epoch=len(train_dataset), step_epoch=[15])
])
optimizer_params = {'lr_scheduler': lr_scheduler,
'learning_rate': 1e-4}
Create Adam solver
The example for depth & pose optimizer are defined as:
The training loop¶
Please checkout the full trainer.py for complete implementation.
This is an example of training loop:
def train(self):
"""Run the entire training pipeline
"""
self.logger.info('Starting Epoch: %d' % self.opt.start_epoch)
self.logger.info('Total Epochs: %d' % self.opt.num_epochs)
self.epoch = 0
for self.epoch in range(self.opt.start_epoch, self.opt.num_epochs):
self.run_epoch()
self.val()
# save final model
self.save_model("final")
self.save_model("best")
def run_epoch(self):
"""Run a single epoch of training and validation
"""
print("Training")
tbar = tqdm(self.train_loader)
train_loss = 0.0
for batch_idx, inputs in enumerate(tbar):
with autograd.record(True):
outputs, losses = self.process_batch(inputs)
mx.nd.waitall()
autograd.backward(losses['loss'])
self.depth_optimizer.step(self.opt.batch_size, ignore_stale_grad=True)
if self.use_pose_net:
self.pose_optimizer.step(self.opt.batch_size, ignore_stale_grad=True)
train_loss += losses['loss'].asscalar()
tbar.set_description('Epoch %d, training loss %.3f' % \
(self.epoch, train_loss / (batch_idx + 1)))
if batch_idx % self.opt.log_frequency == 0:
self.logger.info('Epoch %d iteration %04d/%04d: training loss %.3f' %
(self.epoch, batch_idx, len(self.train_loader),
train_loss / (batch_idx + 1)))
mx.nd.waitall()
You can Start Training Now.
References¶
- Godard17
Clement Godard, Oisin Mac Aodha and Gabriel J. Brostow “Unsupervised Monocular Depth Estimation with Left-Right Consistency.” Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). 2017.
- Godard19(1,2,3,4)
Clement Godard, Oisin Mac Aodha, Michael Firman and Gabriel Brostow. “Digging Into Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation.” Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision (ICCV). 2019.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.262 seconds)